



 Bakersfield, Calif.
|
March 11, 2024 08:00 AM Pacific Daylight Time
Bakersfield, Calif.
|
March 11, 2024 08:00 AM Pacific Daylight Time
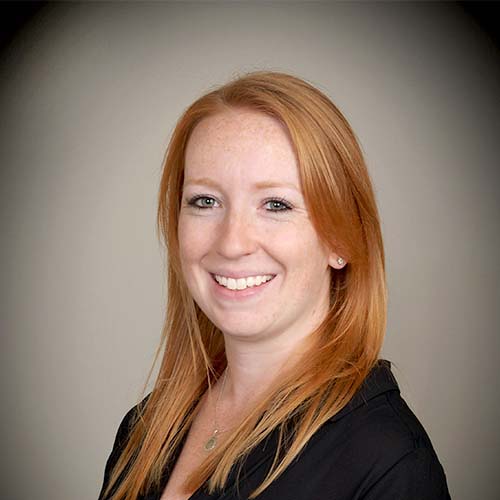

Centre for Neuro Skills (CNS), a leader in traumatic brain injury and stroke rehabilitation services, today announced the promotion of Stefanie N. Howell, Ph.D., CBIS, to director of research integration.
“Stefanie has been integral to Centre for Neuro Skills’ research program, looking closely at how we can not only improve the lives of our patients but people with brain injuries everywhere,” said David Harrington, president and CEO of Centre for Neuro Skills. “I’m excited to see the outcomes of our research efforts and how this can give us new insight into improving patient care.
Since joining CNS in 2016, Howell has coordinated and designed clinical research studies, written manuscripts and provided education focused on methods for facilitating recovery and maximizing patient outcomes. Howell was promoted to Senior Neuroscientist in 2022 and now oversees the integration of CNS’ original research to expand understanding of brain injury, its causes and best treatment practices in the clinical setting.
CNS’ ongoing research includes:
Effects of Rehabilitation Following Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) and Stroke
CNS researchers evaluate the durability of outcomes obtained during post-acute rehabilitation following stroke and TBI. This will also determine if rehabilitation outcome is associated with future occupational status, life quality, cognitive function, and overall health, including rehospitalization.
Traumatic Brain Injury and the Gut Microbiome
Years after a brain injury, some individuals develop a complex set of conditions that prevent them from absorbing essential amino acids. The purpose of this study is to determine if altering the diet in these individuals can change their amino acid absorption and reduce symptoms and markers of neuroinflammation.
Effects Of Aerobic Exercise and Rehabilitation After Traumatic Brain Injury
Exercise contributes to overall health and protects and heals the brain, but the response to exercise may change after a brain injury. Through examining exercise and how it facilitates recovery, CNS hopes to determine the individual response to exercise (and how it has changed), in order to better tailor therapy to each person.
Outcome Biomarkers After Brain Injury
Patients consent to providing biological samples to help identify biomarkers in blood, saliva, and other tissues that will help CNS increase diagnostic and prognostic capabilities, tailor patient care and determine how much treatment is necessary. This study will allow clinicians to foresee potential risks that may inhibit recovery and aid intervention effectiveness, allowing CNS to better evaluate current and novel therapeutic interventions.
Sleep Alterations After Traumatic Brain Injury and Stroke
Sleep-wake disturbances have been identified in up to 80% of those with brain injuries. Sleep problems are linked to impaired attention, decreased cognitive functioning (including memory and attention) and overall diminished response to rehabilitation. This study will determine the nature of sleep-wake disturbances post injury. Researchers may then identify whether disturbances are related to the type, location, or time since the injury, as well as the impact sleep has on outcome and responsiveness to rehabilitation.
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) Following Traumatic Brain Injury
This is a noninvasive technique of neurostimulation, which uses low amplitude direct current to alter brain cell firing. Studies suggest that tDCS is a painless technique for electrically stimulating the brain with almost no risk of harm. This form of therapy has been studied as a treatment modality for stroke patients but there is less evidence in literature for effectiveness in treating traumatic brain injury. This project will analyze the effects of a three-week program of tDCS on motor recovery and attention/concentration in individuals following a traumatic brain injury.
To learn more about CNS and its research, visit www.neuroskills.com.
***
About Centre for Neuro Skills
Centre for Neuro Skills is an experienced and respected world leader in providing intensive rehabilitation and medical programs for those recovering from all types of brain injury. CNS covers a full spectrum of advanced care from residential and assisted living to outpatient/day treatment. Founded by Dr. Mark Ashley in 1980, CNS has seven locations in California and Texas. For more information about Centre for Neuro Skills, visit: www.neuroskills.com, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube.
Media, please note: Visual assets, including photos, are available. To request an interview with CNS leadership or clinical staff, please contact Robin Carr at 415.766.0927 or CNS@landispr.com.
# # #
Contact Details
Landis Communications Inc.
Robin Carr
+1 415-766-0927
Company Website
